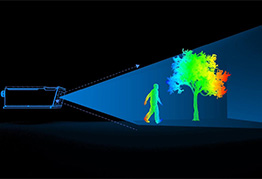
What is PHOTOGRAMMETRY VS LIDAR
Photogrammetry and LiDAR are both technologies used for capturing spatial data, but they differ in their methods of data collection. Photogrammetry involves using photographs taken from different angles to create 3D models of objects or landscapes. This process relies on the principles of triangulation to determine the position of points in space. On the other hand, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) uses laser pulses to measure distances to objects and create detailed 3D maps. LiDAR is often used in applications where high accuracy and precision are required, such as in topographic mapping, forestry management, and urban planning. In summary, photogrammetry is based on photographs while LiDAR uses laser technology for data collection.
The Main Technology in PHOTOGRAMMETRY VS LIDAR
Photogrammetry and LiDAR are two main technologies used for capturing detailed information about the Earth's surface. Photogrammetry involves taking photographs from different angles and using specialized software to create 3D models of the terrain. On the other hand, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) uses laser pulses to measure distances and create highly accurate 3D maps. While photogrammetry is more cost-effective and can capture larger areas, LiDAR provides higher accuracy and works well in challenging environments such as dense forests or urban areas. In summary, both technologies have their strengths and weaknesses, and the choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the project.


Applications of PHOTOGRAMMETRY VS LIDAR
Photogrammetry and LiDAR are both valuable technologies used in various applications, each offering unique advantages. Photogrammetry involves the process of creating 3D models or maps using photographs taken from different angles, while LiDAR uses laser pulses to measure distances and create detailed 3D representations of objects or landscapes. In terms of applications, photogrammetry is commonly used in fields such as archaeology, urban planning, and forestry for its ability to capture detailed imagery and create accurate models. On the other hand, LiDAR is often preferred for applications that require high precision and accuracy, such as topographic mapping, autonomous vehicle navigation, and infrastructure monitoring. Both technologies have their strengths and can be chosen based on the specific requirements of the project at hand.
Benefits of PHOTOGRAMMETRY VS LIDAR
Photogrammetry and LiDAR are both valuable tools for capturing detailed spatial data, but they each have their own unique benefits. Photogrammetry, which involves using photographs to create 3D models, is often more cost-effective and can be easily integrated with existing photography equipment. It also allows for the capture of high-resolution images, making it ideal for applications such as cultural heritage preservation and urban planning. On the other hand, LiDAR technology uses laser pulses to measure distances and create highly accurate point clouds, making it particularly useful for terrain mapping and forestry applications where precise elevation data is required. In summary, the benefits of photogrammetry include cost-effectiveness and high-resolution imaging capabilities, while LiDAR offers superior accuracy and precision in capturing spatial data.

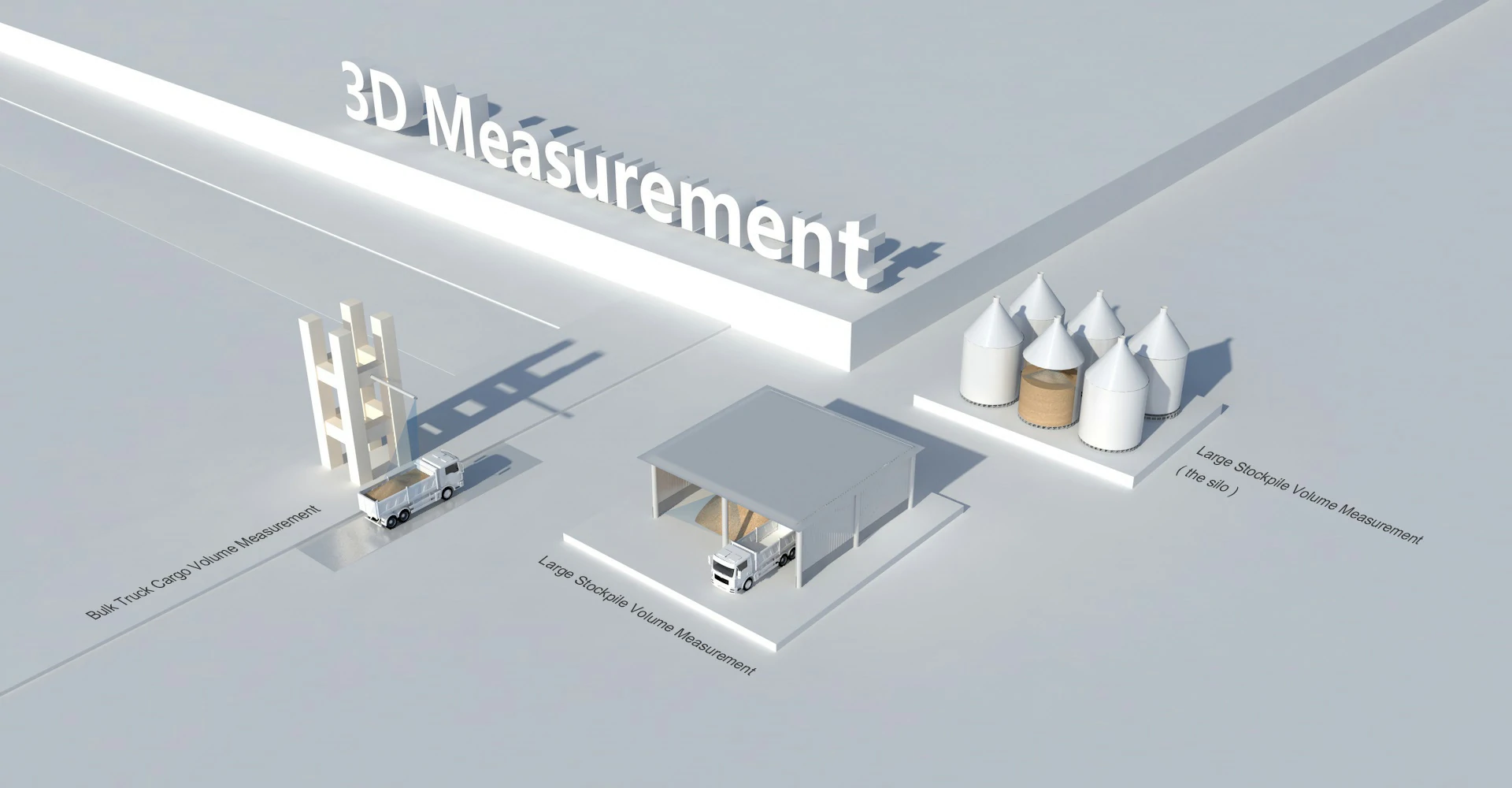
LiDAR in Construction Monitoring
Neuvition's Titan series LiDAR sensors offer high-precision 3D scanning capabilities
ideal for construction site monitoring. The Titan M1 series, with its long-range and
high-resolution features, can capture detailed site data for accurate progress tracking
and volumetric measurements.
Neuvition LiDAR Products Overview

Titan S2
Specialized for specific industrial uses.

NeuX1
Next-generation LiDAR technology with enhanced capabilities.

Titan M1 Series
Long-range, high-resolution LiDAR sensors for various applications.

Titan W1
Designed for wide-angle scanning in challenging environments.

Titan P1
Compact and versatile for mobile and robotics applications.
Neuvition LiDAR Products Overview

Railway Collision Avoidance
Enhancing safety in rail transportation.

Volume Measurement
Accurate 3D volume calculations for industries like mining and construction.

Smart Highway
Improving road safety and traffic management.
Robotics
Enabling precise navigation and object detection for autonomous robots.

Autonomous Driving
Advanced sensing for self-driving vehicles.
Application Areas of LiDAR
Benefits of Using LiDAR

High accuracy and
precision in 3D mapping

Real-time data
collection and processing

Ability to penetrate vegetation
and capture ground topography

Efficient large-scale
surveying and mapping

Enhanced safety in
autonomous systems

Improved decision-making
with detailed spatial information
Software Solutions for LiDAR
Neuvition provides software solutions to complement its hardware, including point cloud processing and analysis
tools, real-time visualization software, a data integration platform for enterprise applications, and customized
algorithms tailored to specific industry needs.

Success Stories
MetroInnovate Urban Solutions improved traffic flow by 15% after implementing Neuvition's Smart Highway system. Emily Parker, the Director of Smart City Development, played a key role in deploying this system to enhance urban traffic management and reduce congestion.

BuildMaster Construction reduced project timelines by 20% using Neuvition's LiDAR-based site monitoring solution. Michael Thompson, the COO, led the adoption of this technology, focusing on improving efficiency and project management.

DeepCore Mining increased excavation efficiency by 25% with Neuvition's volume measurement solution. Robert Lin, the Head of Operations, was instrumental in integrating this technology to optimize resource extraction and operational productivity.

FAQ












Contact Us
If you have any questions or suggestions, please leave a message, we will get in touch with you within 24 hours!